The probability of rolling exactly x same values equal to y out of the set imagine you have a set of seven 12 sided dice and you want to know the chance of.
Roll a die 36 times compute the probability of obtaining exactly 6 sixes.
So the probability is.
You need to roll exactly 2 sixes and 4 other numbers.
15 1 6 2 5 6 4 0 20094.
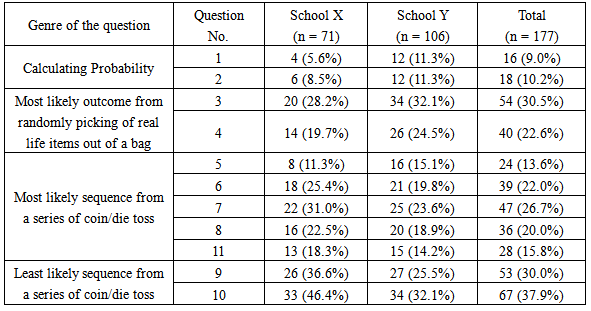
The possible outcomes of rolling two dice are represented in the table below.
Probability table of rolling two dice.
Then the probability is.
The probability of rolling a six on one roll is 1 6.
The roll has 6 sides the probability of rolling a six when the die is rolled once is 1 6 when rolled 4 times each time has a probability of 1 6.
P 3 1 6 ⁿ 1 2 ⁿ.
Note that the number of total possible outcomes is equal to the sample space of the first die 6 multiplied by the sample space of the second die 6 which is 36.
If we take identical conditions s 6 y 3 and apply them in this example we can see that the values 1 2 3 satisfy the rules and the probability is.
The probability that we roll exactly one six is 3 the number of ways to choose which one will be a six the number of one set regions in the diagram times the probability that that roll will be a six 1 6 times the probability that the other two rolls will not be six 5 6 5 6.
Independent probabilities are calculated using.
Also there are 6 choose 2 15 different ways to arrange the rolls.
Probability of both probability of outcome one probability of outcome two so to get two 6s when rolling two dice probability 1 6 1 6 1 36 1 36 0 0278 or 2 78 percent.